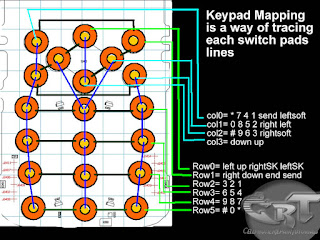
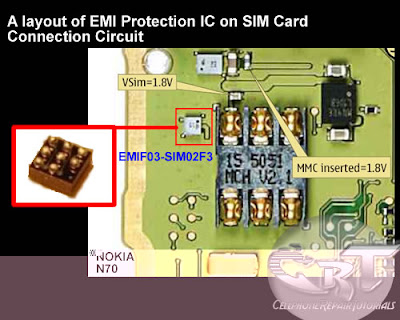
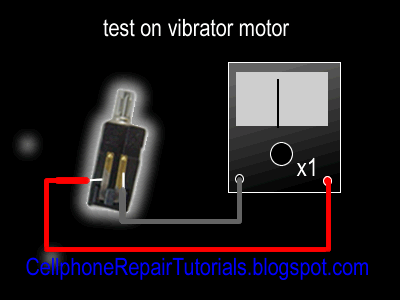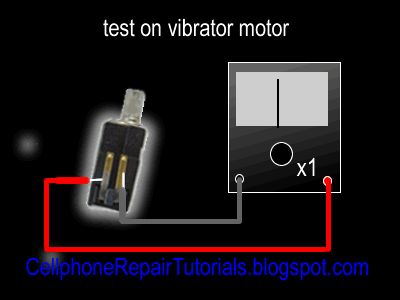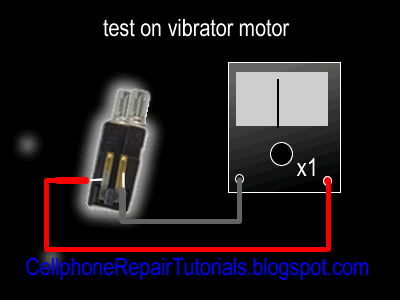
There are few types of charging problem issues like Not Charging, No Charging Response and Charger Not Supported.
A problem issues with "Not Charging" shows on a display when a charger is being plug-in, this problem occurs when a required current or voltage is not enough to boost up and charge the mobile phones battery.
One reason of this problem is a faulty BSI Line, a BSI line is a Battery Size Indicator that tell the charging control circuit how's the batteries working status.
The battery has a BSI output indicator terminal that connected to its negatives terminal with desired value of resistor on it.
One other charging problem issues is the No charging response when a battery charger is being plug-in, it stays no response or nothing happens.
One reason of this is a faulty protection circuit section. this happens when there is no voltage reach to charging circuit indicators and controls. If the protection circuit breakdown this will result to "charging no response" situation. You need to check each components for short and open circuits. You may start from the fuse then to the coil and the diode.
Charger Not Supported problem is cause by a faulty BTEMP thermistor component, BTEMP stands for Battery Temperature, This is the one that monitors the battery temperature status during at charging status, if this one having a problem , it wont allow any charger to proceed to charging stage.
This all, is only a brief explanation of how charging problem issues occurs, while charging the mobile phones .
There are lots of ways on how to troubleshoot each and every kind of handsets. Hope at least, this one let help you understand how charging problem issues occurs, and by this you can gain ideas to move into a stage where you can practice how to troubleshoot this kind of issues.
A problem issues with "Not Charging" shows on a display when a charger is being plug-in, this problem occurs when a required current or voltage is not enough to boost up and charge the mobile phones battery.
One reason of this problem is a faulty BSI Line, a BSI line is a Battery Size Indicator that tell the charging control circuit how's the batteries working status.
The battery has a BSI output indicator terminal that connected to its negatives terminal with desired value of resistor on it.
One other charging problem issues is the No charging response when a battery charger is being plug-in, it stays no response or nothing happens.
One reason of this is a faulty protection circuit section. this happens when there is no voltage reach to charging circuit indicators and controls. If the protection circuit breakdown this will result to "charging no response" situation. You need to check each components for short and open circuits. You may start from the fuse then to the coil and the diode.
Charger Not Supported problem is cause by a faulty BTEMP thermistor component, BTEMP stands for Battery Temperature, This is the one that monitors the battery temperature status during at charging status, if this one having a problem , it wont allow any charger to proceed to charging stage.
This all, is only a brief explanation of how charging problem issues occurs, while charging the mobile phones .
There are lots of ways on how to troubleshoot each and every kind of handsets. Hope at least, this one let help you understand how charging problem issues occurs, and by this you can gain ideas to move into a stage where you can practice how to troubleshoot this kind of issues.